The European Union (EU) has established comprehensive rules and regulations governing healthcare and medical devices to ensure safety, efficacy, and harmonized standards across its member states. EU has long been at the forefront of regulatory standards in various industries, including healthcare. Established in the 1990s, these regulations aim to harmonize standards and ensure the safety and efficacy of products in the European market. These regulations, collectively known as the Medical Device Directive (MDD), require medical device manufacturers to meet essential health, safety and performance requirements in order to receive CE marking certification. The MDD impacts the enabling innovations in the Medtech industry significantly while protecting patient safety through heightened transparency, conformity assessments, and post-market surveillance.
With the growing development and reliance of in vitro diagnostic medical devices, there has been a significant overhaul of regulations governing medical devices within the EU. These changes aim to enhance patient safety, ensure the effectiveness of medical devices, and adapt to advancements in technology.
Need of New Regulations on Medical Devices
While the earlier directives established an important regulatory system for medical devices, advances in technology and evidence of gaps have underscored the need for updated regulations. Complex new devices, ranging from mobile health apps to AI diagnostics, have rapidly changed the trajectory of the healthcare landscape. Furthermore, the incidents associated with the risks of breast implant and high profile safety issues with approved devices like metal hip implants highlighted the weaknesses of the existing regulations, resulting in reduced confidence of patients, consumers, and healthcare professionals on the safety of medical devices. Moreover, reports from whistleblowers alleging ASR implants causing pain and discomfort in patients exposed potential deficiencies in the conformity assessment procedures and post-market surveillance under the existing directives.
To mitigate this and ensure the safety of medical devices, the EU established new regulations to inspect the latest scientific and technological progress and set standards for the global regulation of medical device.
Latest Regulations on Medical Devices
The EU updated its regulations on medical devices in 2012, as the one introduced in the 1990s, were outdated due to technological advancements. The regulations, proposed in 2012 replaced three existing directives to tighten controls on safety and effectiveness. Furthermore, the new EU Medical Device Regulations (MDR) (2017/745) replaced the EU Medical Device Directive (MDD) and Active Implantable Medical Device Directive (AIMD) to come into effect in May 2021. The new regulation focused on improving quality, safety, and transparency. The regulation imposes reporting rules on substances used to design and make medical devices, though intravenous (IV) devices are excluded. The goal is to decrease possible hazards from these materials. The EU MDR applies to devices, components, or materials within devices that either: enter the body and touch it, give or resupply medicines, body fluids or other substances, or are used to hold or transport such liquids.
Here are some key implementing measures and an overview of the expected changes from these measures:
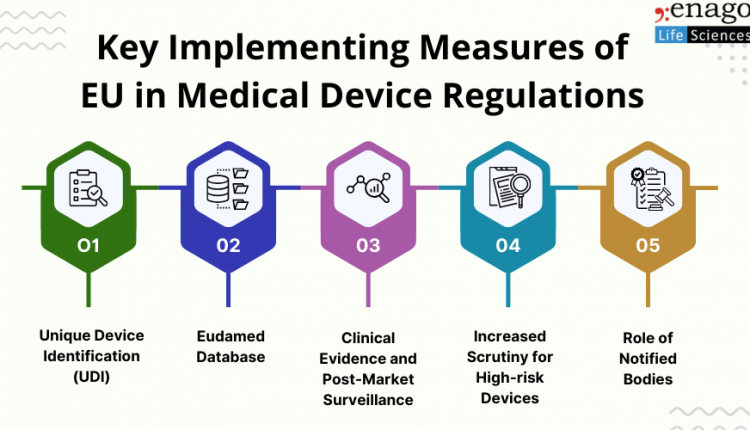
1. Unique Device Identification (UDI)
One of the pivotal changes introduced by the new regulations is the mandatory implementation of a Unique Device Identification (UDI) system. The UDI aims to enhance traceability and facilitate the efficient monitoring of medical devices throughout their lifecycle. Manufacturers are required to assign a unique identifier to each device, providing crucial information about its origin, characteristics, and intended use.
2. Eudamed Database
The European Database on Medical Devices (Eudamed) has been revamped to serve as a central repository for information related to medical devices. The database facilitates the exchange of information among member states, competent authorities, and other stakeholders. Manufacturers must submit detailed information about their products to ensure transparency and streamline regulatory processes.
3. Clinical Evidence and Post-Market Surveillance
The MDR emphasizes on clinical evidence and post-market surveillance to ensure the ongoing safety and performance of medical devices. Manufacturers are now required to conduct more rigorous clinical evaluations and actively monitor their products once they are on the market. This shift aims to identify and address potential issues promptly, minimizing risks to patients.
4. Increased Scrutiny for High-risk Devices
High-risk medical devices, such as implantable devices, pacemakers, and certain in vitro diagnostics, undergo a more thorough pre-market scrutiny process. This involves the involvement of notified bodies and, in some cases, consultation with expert panels. The goal is to ensure that these devices meet the highest standards of safety and performance before entering the market.
5. Role of Notified Bodies
Notified bodies play a crucial role in the new regulatory framework. They are responsible for assessing the conformity of medical devices with the regulations. However, the new regulations demand more stringent requirements for notified bodies, including increased competency and transparency, to strengthen their role in the certification process.
Benefits Offered by the Latest Regulations
The new regulations paves way to transparency and prioritizes protection of patient information. The key improvements of this movement include enhanced protection for public health and patient safety, especially for high-risk devices. Aesthetic devices and practices like reprocessing single-use devices are brought under stricter and more harmonized regulations. Rules on clinical evaluation and investigation are strengthened, along with stricter requirements on hazardous substances. Furthermore, a real-time, comprehensive database was set that offers insights into the details of all medical products in the EU market.
The new regulations prioritize a patient-friendly environment, emphasizing transparency, information, and choice. Notable benefits include enhanced protection for public health and patient safety, particularly for high-risk devices, and a more rigorous approach to aesthetic devices. Strengthened rules on clinical evaluation, investigation, and hazardous substances contribute to overall safety improvements.
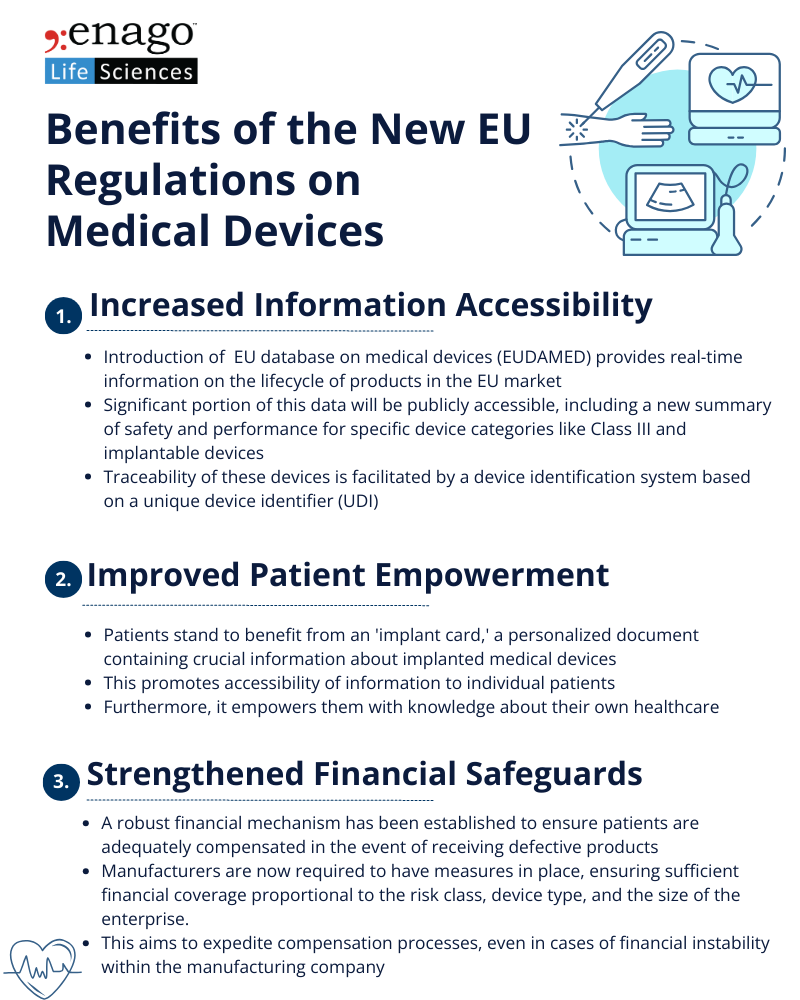
These regulations not only enhance patient safety but also prioritize transparency, information accessibility, and financial safeguards to create an improved and patient-centric healthcare environment. While the new regulations aim to enhance patient safety and ensure the effectiveness of medical devices, their implementation poses challenges for manufacturers. The transition to the new regulatory framework requires significant adjustments in processes, documentation, and compliance strategies. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), in particular, may face resource constraints in meeting the new requirements.
The recent developments in implementing measures for EU Medical Device Regulations represent a landmark shift in the regulation of medical devices. The focus on enhanced transparency, rigorous pre-market scrutiny, and robust post-market surveillance underscores the EU’s commitment to ensuring the safety and efficacy of medical devices.
References:
- “31993L0042.” EUR. Accessed January 23, 2024. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A31993L0042.
- Cohen, D. “Out of Joint: The Story of the Asr.” BMJ 342, no. may13 2 (May 14, 2011): d2905–d2905. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.d2905.
- “Medical Devices.” Medical devices | European Medicines Agency. Accessed January 19, 2024. https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/human-regulatory-overview/medical-devices#:~:text=The%20Regulations%20on%20Medical%20Devices,certain%20categories%20of%20medical%20device.
- “Medical Devices Regulation (EU) 2017/745 – MDR.” DNV. Accessed January 19, 2024. https://www.dnv.com/services/medical-devices-regulation-eu-2017-745-mdr-138310#:~:text=The%20transition%20date%20is%20currently,medical%20device%20quality%20management%20system).
Author:

Anagha Nair
Editorial Assistant, Enago Academy
Medical Writer, Enago Life Sciences
Connect with Anagha on LinkedIn

